Doron Behar, postdoctoral fellow in the Hebrew University of Jerusalem, and William Hurst, administrator of the mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) Haplogroup K Project, discussed the use of mtDNA testing for genealogy and anthropology.
Doron Behar, MD, PhD
SOURCE: Doron Behar, MD, PhD (Houston, Harris County, Texas). Photographed by Stephen J. Danko on 14 March 2009.
William R. Hurst
SOURCE: William R. Hurst (Houston, Harris County, Texas). Photographed by Stephen J. Danko on 14 March 2009.
The mitochondrial genome is a circular unit of DNA with 16569 base pairs numbered according to the Cambridge Reference Sequence (CRS). Two hypervariable segments (HVS-I from bp 16029-16383 and HVS-II from bp 00057-00372) make up the bulk of the control region (bp 16024-00372).
Haplotypes are determined from short tandem repeats (STRs) in HVS-I, and haplogroups are determined from single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in the coding region of the mitochondrial genome.
GenBank has over 5100 complete mtDNA sequences, 250 of which are from Family Tree DNA (FTDNA). By itself, FTDNA has over 4100 complete mtDNA sequences. These sequences were used in the studies published as Olivieri A, et al. (2006) The mtDNA legacy of the Levantine early Upper Paleolithic in Africa. Science 314:1767-1770 and Behar D., R. Villems, H. Soodyall, J. Blue-Smith, L. Pereira, E. Metspalu, R. Scozzari, H. Makkan, S. Tzur, D. Comas. 2008 The Dawn of Human Matrilineal Diversity. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 82:1130-1140.
The HVS-I mutation rate is about 1 mutation per 20,000 years; the coding region mutation rate is about 1 mutation per 5000 years, and the overall mtDNA mutation rate is about 1 mutation per 4000 years.
Based on analyses of mtDNA, there are four surviving populations in Africa today: the Pygmies, the Khoisan, African non-Pygmy or Khoisan, and non-Africans. About 95% of West Central African Pygmies and 20% of West Central African Bantus belong to the L1c1a clade and can be dated to about 75,000 years before the present (ybp). The L0d and L0k clades correspond to Khoi or San ancestry and date back to 90,000 ybp. Clades L3M and L3N gave rise to the entire out of Africa lineage.
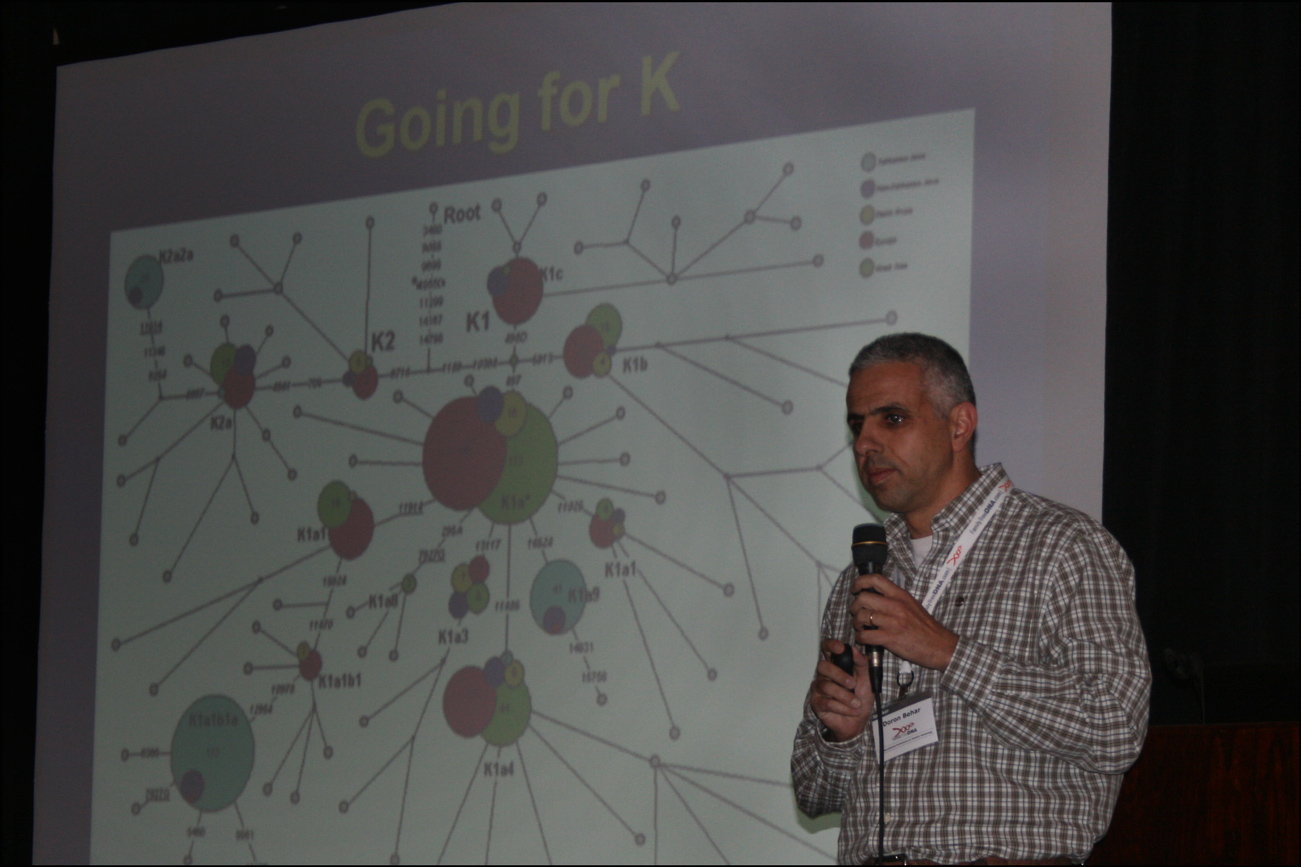
A detailed study of one of these out of Africa lineages, designated as Haplogroup K, was conducted based on full mtDNA sequences. Haplogroup K was distributed throughout western Eurasia and is the haplogroup to which about 1/3 of all Ashkenazi Jews belong. Currently, there are 43 K subclades. Based on the full mtDNA sequences obtained, 88 new K subclades have been identified for a total of 131 total K subclades.
Full mitochondrial sequences provide data that can identify new SNPs and, therefore, establish new subclades. The identification of new mtDNA subclades may enable genetic genealogists to provide more refined information on ancestry than is currently available through mtDNA analysis.
Copyright © 2009 by Stephen J. Danko